- The Trump administration is headed to the United Nations in an attempt to have tough sanctions reinstated against Iran
- The U.S. is looking to execute a clause in the Iran nuclear deal which allows punitive measures to be taken if terms are not met
- Iran admits to going against certain parts of the agreement but says it’s only done so because of sanctions imposed after the U.S. pulled out of the deal
- But, Russia, China and the E.U. don’t support the sanctions, arguing the U.S. has no standing after leaving the nuclear deal in 2018
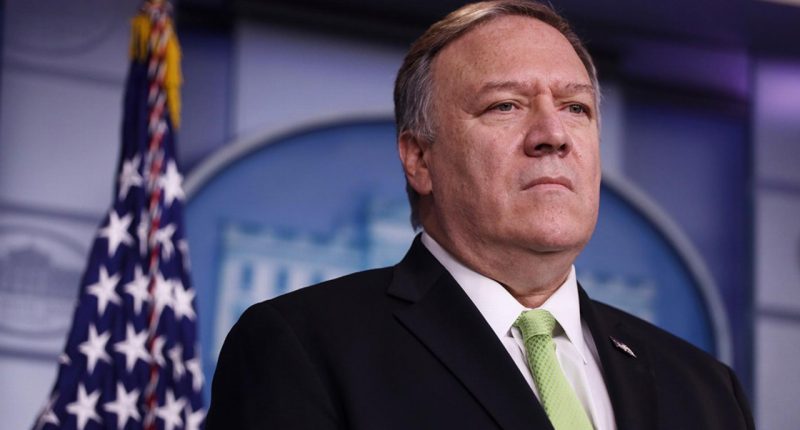
The Trump administration is headed to the United Nations in an attempt to have tougher sanctions reinstated against Iran.
As part of the push, U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo will front the Security Council to request a “snapback” to sanctions as outlined under the 2015 Iran nuclear deal, known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
But the U.S. unilaterally withdrew from the deal two years ago, leading other Security Council members to ask whether the U.S. can enforce the clause, given it’s no longer party to the deal.
Uphill battle
Last week, the U.S.’s attempt to extend the Iranian arms embargo beyond October was blocked in the UN – with only the Dominican Republic backing the motion.
In an attempt to shore up support, the U.S. had scrubbed anti-Iran rhetoric from the proposal, but the deal was still sunk after Russia and China voted it down, and 11 other UN members abstained.
At the time, the U.S. Secretary of State issued a statement even before the vote had been finalised, criticising the international community for not jumping on board.
“The Security Council’s failure to act decisively in defence of international peace and security is inexcusable,” Mike Pompeo said.
Standing alone
Now, the snapback to sanctions faces a similar uphill battle, with Russia and China again opposed to the move, and other member states not willing to throw their support behind the motion.
This is because the validity of the U.S.’s proposal to bring back the sanctions has been called into question — as the country opted to leave the deal it’s trying to enforce in 2018.
The U.S. argues the action is permissible as it has a permanent membership with the Security Council, which originally ratified the accord.
However, a European Commission statement said the U.S. has no standing to raise issues on the Iran deal since it pulled out.
“The U.S. cannot be considered as a JCPOA participant […] we, therefore, consider that the U.S. is not in a position to resort to mechanisms reserved for JCPOA participants.”
Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi agreed and said the U.S. “has no right to demand the Security Council to activate the rapid reinstatement of sanctions mechanism.”
The U.S. Secretary of State is expected to present evidence Iran has flouted the terms of the agreement — a charge Iran does not deny.
But Iran does argue those actions have only come about because of sanctions imposed by the U.S. after withdrawing from the deal.
Mike Pompeo is set to meet with Indonesia’s U.N. Ambassador, Dian Triansyah Djani, and U.N. Secretary-General, Antonio Guterres, on Thursday, to submit the clause.