- Twenty Seven Co (TSC) begins a geochemical sampling program at the Trident Project in New South Wales
- This work is focused on multiple lithium-caesium-tantalum (LCT) pegmatites after TSC found lithium anomalies via a historical data review
- The company says this project has seen little exploration so this program will allow it to better understand the geology of the greater tenement package
- Over the next few months, TSC will analyse the results to inform next steps, as well as begin drilling and sampling at the Rover Project in WA
- Company shares are up 10 per cent to trade at 0.6 cents at 12:09 pm AEST
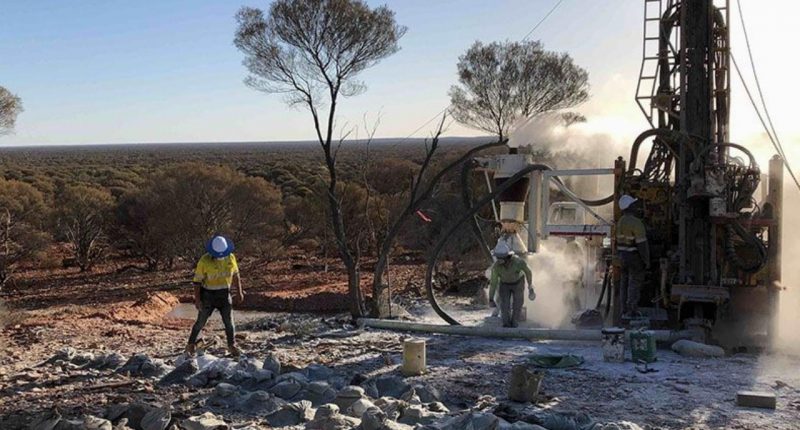
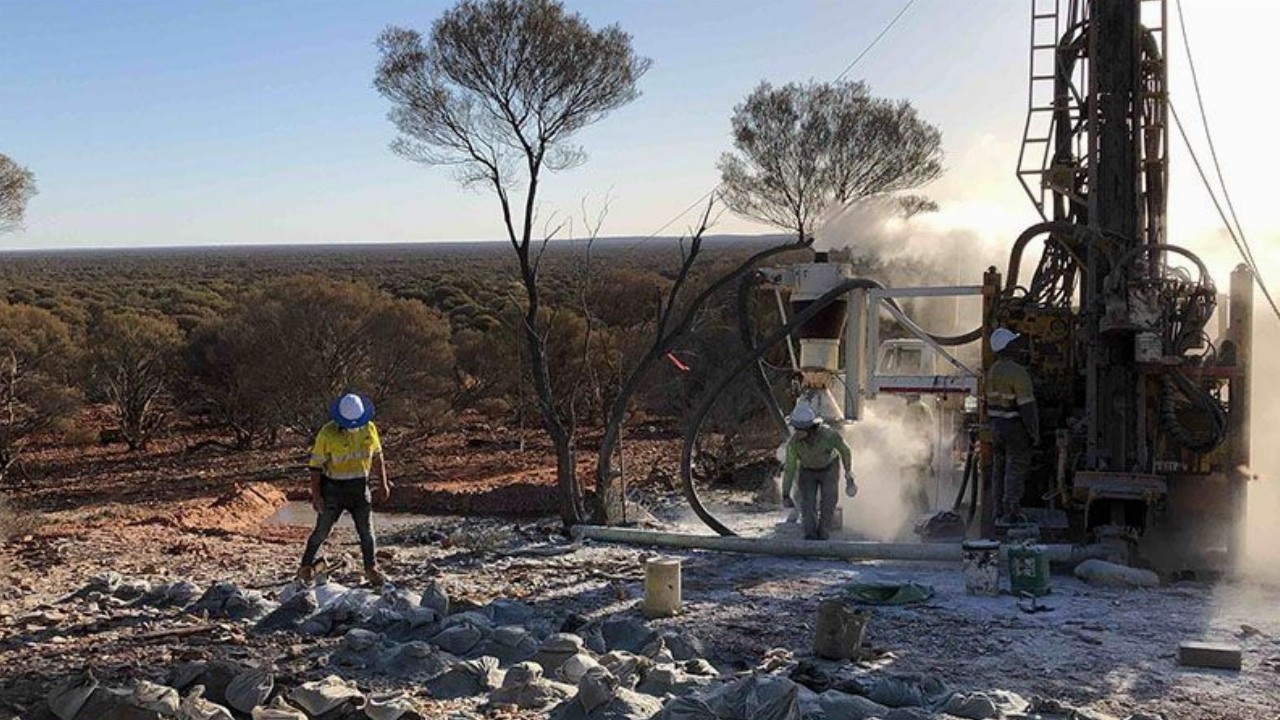
Twenty Seven Co (TSC) has begun a geochemical sampling program at the Trident Project in New South Wales.
This program follows the recent discovery of multiple new lithium and tin targets through a review of historical geochemical data.
As announced earlier this month, Twenty Seven Co found historical rock chip sample results with values ranging between 1.56 and 7.63 per cent lithium dioxide.
The new anomalies have coincidental lithium, caesium and tantalum (LCT) with niobium and tin, which suggests the presence of LCT pegmatites.
Previous explorers sampled the LCT pegmatites which show that lithium occurs within amblygonite and lesser spodumene, which are both important minerals for lithium mining.
CEO Simon Phillips commented on the sampling program.
“We are delighted to have our team on the ground at Trident and we are looking forward to investigating several high priority lithium and tin targets with this initial sampling program,” he said.
“Minimal historical work has been completed across this project, so this sampling program will significantly add to the geological knowledge of the greater tenement package.”
Over the next few months, Twenty Seven Co plans to analyse and interpret the sampling results to inform next steps. It will also begin drilling anomalies and conduct geochemical sampling at the WA-based Rover Project.
Company shares are up 10 per cent to trade at 0.6 cents at 12:09 pm AEST.